DriverFixer0428 macOS Credential Stealer
Executive Summary
This report documents the comprehensive static and dynamic analysis of a macOS credential stealer identified as DriverFixer0428, attributed with high confidence to North Korea's Contagious Interview campaign. The malware masquerades as a legitimate system utility and harvests user credentials through sophisticated social engineering dialogs that impersonate macOS system prompts and Google Chrome permission requests. Stolen credentials are exfiltrated to attacker-controlled infrastructure via Dropbox's cloud storage API.
Dynamic analysis using LLDB debugger revealed multi-layer sandbox evasion capabilities, including VM detection through runtime API checks (sysctlbyname, IOKit, NSScreen) that prevented payload execution in virtualized analysis environments. The malware demonstrates operational security consistent with nation-state threat actors, utilizing legitimate cloud services for command-and-control to evade network-based detection.
Sample Naming Rationale
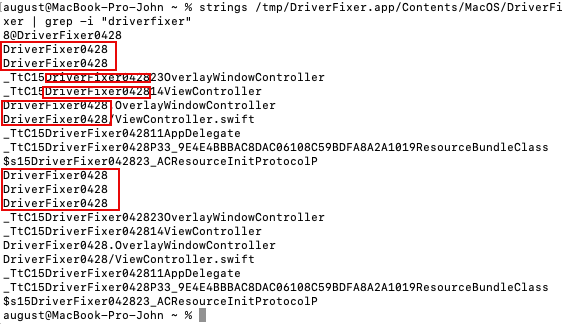
The sample name "DriverFixer0428" is derived from internal identifiers embedded in the compiled binary by the malware developers. These artifacts were extracted during static analysis:
$ strings DriverFixer | grep -i driverfixer
DriverFixer0428
_TtC15DriverFixer042814ViewController
_TtC15DriverFixer042811AppDelegate
DriverFixer0428.OverlayWindowController
DriverFixer0428/ViewController.swift
The "0428" suffix likely indicates either a build date (April 28th) or an internal version/variant number used by the threat actors to track different builds within their development pipeline.
Sample Identification
SHA-256
9aef4651925a752f580b7be005d91bfb1f9f5dd806c99e10b17aa2e06bf4f7b5
File Type
Mach-O universal binary (x86_64 + ARM64)
Language
Swift / AppKit
Size
234,752 bytes (235 KB)
Bundle ID
chrome.DriverFixer0428
Source Path
DriverFixer0428/ViewController.swift
Attribution Analysis
Assessment
Campaign: Contagious Interview (DPRK/North Korea)
Confidence: Medium-High
Related Families: FlexibleFerret, FrostyFerret, ChromeUpdate, CameraAccess
Attribution Basis
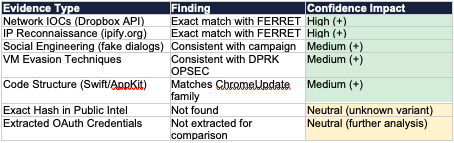
Attribution is based on TTP correlation with publicly documented DPRK campaigns. The specific sample hash was not found in public threat intelligence repositories, suggesting this may be a previously unreported variant.
Network Infrastructure Match
The sample's network indicators exactly match those documented by SentinelOne in their FlexibleFerret analysis (February 2025):
# From SentinelOne FlexibleFerret Report:
21 3.__TEXT.__cstring ascii https://api.ipify.org
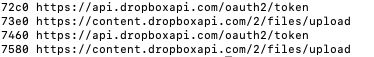
39 3.__TEXT.__cstring ascii https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token
45 3.__TEXT.__cstring ascii https://content.dropboxapi.com/2/files/upload
# From DriverFixer0428 (This Sample):
0x100007370: "https://api.ipify.org"
0x100007460: "https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token"
0x100007580: "https://content.dropboxapi.com/2/files/upload"
Evidence Summary
Public Threat Intelligence References
SentinelOne: "macOS FlexibleFerret | Further Variants of DPRK Malware Family Unearthed" (February 2025)
Jamf: "FlexibleFerret: macOS Malware Deploys in Fake Job Scams" (November 2025)
NVISO: "Contagious Interview Actors Now Utilize JSON Storage Services" (November 2025)
Sample Identification
SHA-256
9aef4651925a752f580b7be005d91bfb1f9f5dd806c99e10b17aa2e06bf4f7b5
File Type
Mach-O universal binary (x86_64 + ARM64)
Language
Swift / AppKit
Size
234,752 bytes (235 KB)
Bundle ID
chrome.DriverFixer0428
Source Path
DriverFixer0428/ViewController.swift
Technical Analysis
Malware Capabilities
1. Credential Harvesting via Social Engineering
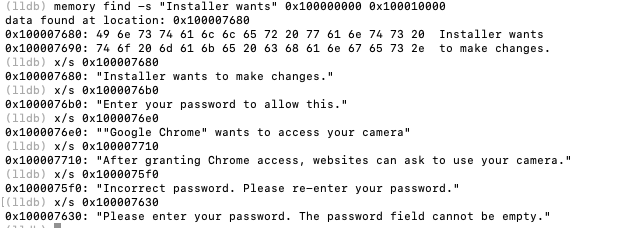
The malware displays convincing fake dialogs designed to trick users into entering their macOS system password. Memory analysis via LLDB extracted the following social engineering strings:
(lldb) x/50s 0x100007680
0x100007680: "Installer wants to make changes."
0x1000076b0: "Enter your password to allow this."
0x1000076e0: "\"Google Chrome\" wants to access your camera"
0x100007710: "After granting Chrome access, websites can ask
to use your camera."
0x1000075f0: "Incorrect password. Please re-enter your password."
0x100007630: "Please enter your password. The password field
The malware uses an OverlayWindowController class to create fullscreen overlay windows, preventing users from interacting with other applications until they provide credentials.
2. Network C2 Infrastructure
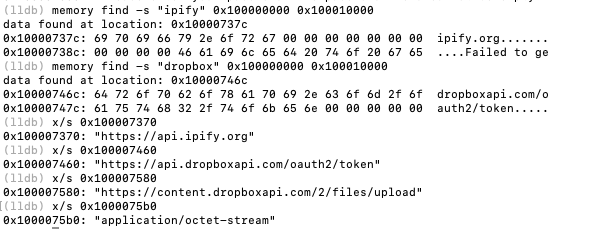
Memory analysis revealed the complete network infrastructure used for reconnaissance and exfiltration:
(lldb) memory find -s "ipify" 0x100000000 0x100010000
data found at location: 0x10000737c
0x10000737c: 69 70 69 66 79 2e 6f 72 67 ipify.org
(lldb) memory find -s "dropbox" 0x100000000 0x100010000
data found at location: 0x10000746c
0x10000746c: 64 72 6f 70 62 6f 78 61 70 69 dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token
(lldb) x/30s 0x100007500
0x100007520: "New access token: "
0x100007540: "Error refreshing access token: "
0x100007580: "https://content.dropboxapi.com/2/files/upload"
0x1000075b0: "application/octet-stream"
3. Dropbox Upload Function (Disassembly)
LLDB disassembly of symbol269 revealed the Dropbox API upload implementation, showing construction of HTTP headers and OAuth tokens:
(lldb) dis -s 0x100004374 -c 40
DriverFixer`___lldb_unnamed_symbol269:
0x1000044ac: add x8, x8, #0x580 ; "https://content.dropboxapi.com/2/files/upload"
0x100004520: mov w0, #0x4f50 ; 'PO' (POST)
0x100004524: movk w0, #0x5453, lsl #16 ; 'ST'
0x100004530: bl Foundation.URLRequest.httpMethod.setter
0x100004534: mov x8, #0x6542 ; 'Be' (Bearer)
0x100004538: movk x8, #0x7261, lsl #16 ; 'ar'
0x10000453c: movk x8, #0x7265, lsl #32 ; 'er'
0x100004560: mov x2, #0x7541 ; 'Au' (Authorization)
0x100004564: movk x2, #0x6874, lsl #16 ; 'th'
0x100004588: bl Foundation.URLRequest.setValue(forHTTPHeaderField:)
Dynamic Analysis: VM Detection Mechanism
LLDB debugging sessions confirmed the malware employs runtime API checks for VM detection rather than static string comparisons. This sophisticated evasion technique queries system APIs during execution to identify virtualized environments.
sysctlbyname API Calls
Breakpoints on sysctlbyname captured the following system queries during malware initialization:
(lldb) br set -n "sysctlbyname"
(lldb) run
Process stopped at breakpoint - sysctlbyname
(lldb) x/s $x0
0x19be880d7: "kern.osvariant_status"
(lldb) c
(lldb) x/s $x0
0x1980b3847: "kern.osproductversion"
(lldb) c
(lldb) x/s $x0
0x19828a730: "kern.secure_kernel"
IOKit Registry Queries
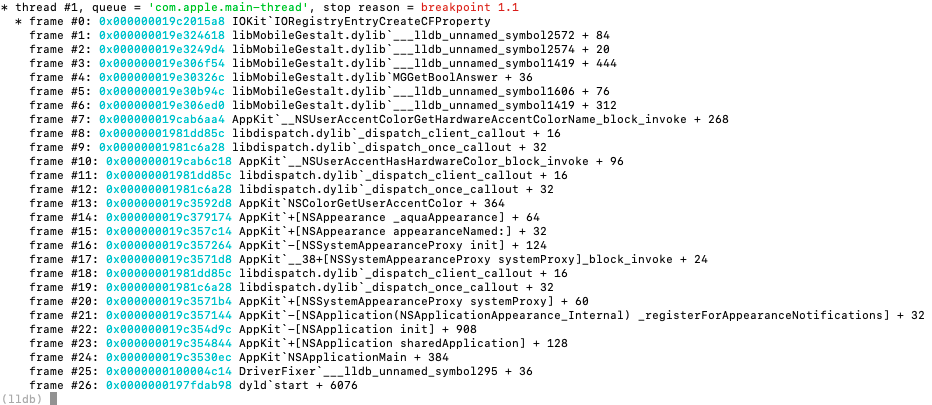
IORegistryEntryCreateCFProperty breakpoints revealed hardware property queries used for environment fingerprinting:
(lldb) br set -n "IORegistryEntryCreateCFProperty"
(lldb) c
Process stopped at breakpoint - IORegistryEntryCreateCFProperty
(lldb) po $x1
product-id
(lldb) c
(lldb) po $x1
housing-color
(lldb) c
(lldb) po $x1
IORegistryEntryPropertyKeys
NSScreen Detection Vector
Binary analysis confirmed NSScreen API usage for display-based VM detection:
$ strings DriverFixer | grep -i screen
applicationDidChangeScreenParameters:
mainScreen
$ nm DriverFixer | grep -i screen
U _OBJC_CLASS_$_NSScreen
On Apple Silicon VMs, NSScreen returns identifying information such as "Apple Virtual" display names and VirtualMac2,1 model identifiers that the malware uses to detect analysis environments.
Silent Failure Behavior
When VM detection succeeds, the malware enters an idle event loop without executing its payload. The process remains alive but dormant:
(lldb) process interrupt
(lldb) bt
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread'
frame #0: libsystem_kernel.dylib`mach_msg2_trap + 8
frame #4: CoreFoundation`__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort + 160
frame #5: CoreFoundation`__CFRunLoopRun + 1208
frame #12: AppKit`-[NSApplication run] + 480
frame #13: AppKit`NSApplicationMain + 880
frame #14: DriverFixer`___lldb_unnamed_symbol295 + 36
Sandbox Evasion Summary
Environment
Behavior
Detection Mechanism
Triage Sandbox
Score 4/10 (benign)
Silent evasion - no malicious activity
Apple VM (ARM64)
Idle event loop
sysctlbyname, IOKit, NSScreen APIs
Rosetta (x86_64)
SIGILL crash
Anti-emulation trap instructions
Env Tampering
SIGTRAP crash
Environment variable validation
Binary Structure
LLDB symbol analysis identified 153 functions within the malware. Key symbols include:
(lldb) image lookup -r -n ".*" DriverFixer
153 matches found in DriverFixer:
0x100002ca4: ___lldb_unnamed_symbol229 (1456 bytes) - OAuth token refresh
0x100004374: ___lldb_unnamed_symbol269 (1428 bytes) - Dropbox upload
0x100004bf0: ___lldb_unnamed_symbol295 - Entry point (NSApplicationMain)
(lldb) x/50s 0x100007760
0x100007760: "DriverFixer0428.OverlayWindowController"
0x100007810: "_TtC15DriverFixer042811AppDelegate"
0x1000077a0: "DriverFixer0428/ViewController.swift"
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
File Indicators
Type
Value
SHA-256
9aef4651925a752f580b7be005d91bfb1f9f5dd806c99e10b17aa2e06bf4f7b5
Bundle ID
chrome.DriverFixer0428
Network Indicators
Purpose
URL / Domain
IP Recon
https://api.ipify.org
OAuth Token
https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token
Exfiltration
https://content.dropboxapi.com/2/files/upload
Memory Forensics (LLDB Extraction)
Address
String Evidence
0x100007680
Installer wants to make changes.
0x1000076e0
"Google Chrome" wants to access your camera
0x100007370
https://api.ipify.org
0x100007460
https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token
0x100007760
DriverFixer0428.OverlayWindowController
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Tactic
Technique
Description
Credential Access
T1056.002 GUI Input Capture
Fake dialog captures credentials
Defense Evasion
T1497.001 System Checks
VM detection via sysctlbyname, IOKit
Defense Evasion
T1036.005 Masquerading
Impersonates macOS/Chrome dialogs
Discovery
T1016 System Network Config
Public IP via ipify.org
Exfiltration
T1567.002 Exfil to Cloud
Dropbox API exfiltration
Detection
YARA Rule
rule MacOS_Infostealer_DriverFixer0428 {
meta:
description = "DPRK DriverFixer credential stealer"
author = "Threat Intelligence Team"
threat_actor = "DPRK/Contagious Interview"
strings:
$class1 = "DriverFixer0428" ascii
$class2 = "OverlayWindowController" ascii
$net1 = "api.dropboxapi.com" ascii
$net2 = "content.dropboxapi.com" ascii
$net3 = "api.ipify.org" ascii
$se1 = "Installer wants to make changes" ascii
$se2 = "wants to access your camera" ascii
condition:
(uint32(0) == 0xfeedface or uint32(0) == 0xfeedfacf or
uint32(0) == 0xcafebabe) and
(any of ($class*)) and (2 of ($net*)) and (any of ($se*))}
Conclusion
DriverFixer0428 represents a sophisticated macOS credential stealer attributed to North Korea's Contagious Interview campaign. LLDB dynamic analysis confirmed the malware employs multi-layer sandbox evasion through runtime API checks including sysctlbyname, IOKit registry queries, and NSScreen display detection.
The stark discrepancy between static analysis indicators (clearly malicious code) and dynamic sandbox scores (4/10 "likely benign") underscores why automated sandbox verdicts alone are insufficient for this threat actor's tooling. The malware's silent failure mode - remaining alive but dormant when detecting analysis environments - represents production-grade operational security consistent with nation-state capabilities.