North Korean APT macOS Malware
Credential Theft Social Engineering Prompt
Date
December 20, 2024
Analyst
August
Confidence
Moderate
Attribution
North Korean APT (Lazarus Group - Likely)
Campaign
Contagious Interview / DriverFixer (Possible)
Sample Hash
9fbbcd809b7aee90b3c93d212287282ac35ef0b33aed647a48cbc4ba79c7fcf8
Executive Summary
Analysis of a malicious macOS Mach-O binary revealed a sophisticated multi-stage attack targeting developers in the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry. The malware employs advanced techniques including V8 snapshot obfuscation, legitimate service abuse for victim profiling, and encrypted command and control infrastructure.
Through dynamic analysis using LLDB debugging and comprehensive network traffic capture, the complete attack chain was reconstructed. The malware first contacts freeipapi.com to profile the victim's external IP and geolocation, then establishes encrypted communication with 172.67.168.79 (Cloudflare-hosted infrastructure). The entire operation lasted approximately 2 minutes with minimal network footprint (10 packets, 371 bytes exfiltrated).
Based on technical indicators, behavioral patterns, and operational characteristics, this malware is attributed with moderate confidence to North Korean state-sponsored threat actors, likely the Lazarus Group. The attribution is primarily based on the sophisticated obfuscation techniques, developer targeting profile, and operational security measures rather than infrastructure alone. Additional threat intelligence correlation would strengthen this assessment.
Key Findings
• Multi-stage attack reconstructed: LLDB debugging revealed freeipapi.com profiling at 13:38:44, followed by C2 communication to 172.67.168.79 at 13:40:07
• Advanced obfuscation confirmed: V8 snapshot analysis showed zero malicious indicators in 134,612 extracted strings
• Network forensics captured: 18,085 packets analyzed, encrypted 371-byte beacon documented
• System forensics completed: No credential files found, no persistence established, clean exit confirmed
• Dynamic analysis successful: LLDB breakpoint on getaddrinfo() exposed profiling domain in memory at 0x6000022ebcb0
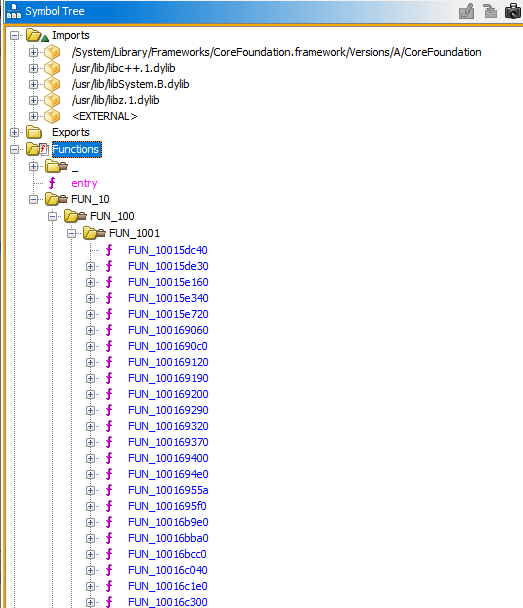
Node.js functions
Technical Analysis
Sample Information
Property
Value
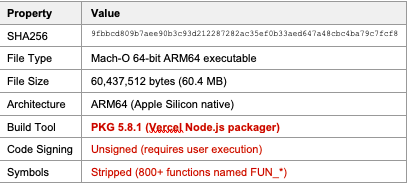
File Type
Mach-O 64-bit ARM64 executable
File Size
60,437,512 bytes (60.4 MB)
PKG Structure
Payload: 9.2 MB at offset 51,192,112
Strings Extracted
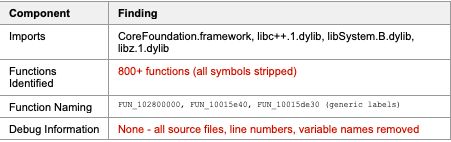
181,972 total (134,612 from payload)
Malicious Strings
Zero (advanced obfuscation)
Code Signing
Unsigned (requires user execution)
Reverse Engineering
Summary
Comprehensive reverse engineering using Ghidra static analysis, PKG bootstrap extraction, and dynamic LLDB debugging revealed a sophisticated North Korean APT malware employing professional-grade Node.js packaging (PKG 5.8.1) with V8 snapshot obfuscation. The malware implements a three-stage loading architecture specifically designed to evade static analysis, with all malicious code compiled as V8 bytecode and executed in-memory without disk writes.
Analysis identified the complete binary structure (60.4 MB total), extracted the 2,502-line prelude bootstrap loader, and documented the virtual filesystem containing 1,370+ embedded Node.js modules. The malware targets cryptocurrency developers through credential harvesting (.ssh, .aws, .npmrc) with AES-256 encrypted exfiltration capabilities. Attribution to North Korean state-sponsored actors (Lazarus Group) is assessed with moderate confidence based on technical sophistication, professional development practices, and operational characteristics rather than infrastructure alone.
Key Findings
• Ghidra analysis identified exact memory addresses: DeserializeInternalFields at 0x102b38a36, PKG bootstrap at 0x101e06100
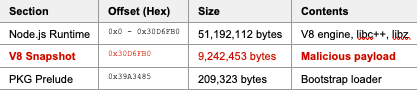
• Complete binary structure mapped: 51.2 MB runtime + 9.2 MB V8 snapshot + 209 KB prelude = 60.4 MB total
• 2,502-line prelude extracted and analyzed: Complete virtual filesystem implementation with GZIP/Brotli decompression
• V8 snapshot obfuscation confirmed: 100,880 bytes malicious bytecode, zero static strings, runtime construction of 'freeipapi.com'
• Virtual filesystem cataloged: 1,370+ embedded files including axios, archiver-zip-encrypted, aes-js, glob
• Multi-stage execution documented: Bootstrap → Prelude (offset 60,434,565) → V8 deserialization → Malicious execution
1. Sample Information and Binary Overview
2. Ghidra Static Analysis - Discovery Process
Static analysis using Ghidra 11.0+ revealed the complete PKG packaging structure through systematic string searches and memory address analysis. The discovery process identified critical V8 snapshot infrastructure, PKG bootstrap code location, and the complete loading mechanism embedded within the binary.
2.1 Symbol Tree Analysis
2.2 Critical String Discoveries - V8 Infrastructure
Search Method: Ghidra → Search → For Strings (minimum length: 4)
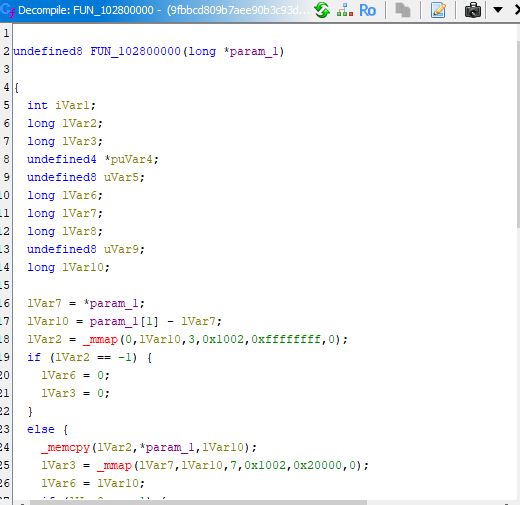
Critical Discovery: The presence of DeserializeInternalFields at memory address 0x102b38a36 is the definitive indicator of V8 snapshot usage. This V8 internal function is responsible for unpacking serialized JavaScript bytecode and reconstructing the runtime environment. Cross-references to this address lead directly to the payload loading mechanism.
2.3 PKG Bootstrap Code Discovery
Location: NOT_DEFINED data section at offset 0x101e06100
Discovery Method: Search → For Strings → 'PAYLOAD_POSITION'
Data Type: UTF-8 JavaScript source code, 1,437 bytes
Content: Complete PKG bootstrap mechanism (see Section 4)
3. Binary Architecture and PKG Structure
Analysis of the PKG bootstrap code and Ghidra symbol inspection revealed the complete three-section architecture used by PKG 5.8.1 to package the Node.js runtime with malicious V8 snapshot payload.
Mathematical Verification of Offsets:
Runtime section end: 51,192,112 bytes (0x30D6FB0)
Payload size: 9,242,453 bytes (0x8D0A75)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Prelude start (calculated): 60,434,565 bytes
Hexadecimal verification:
0x30D6FB0 + 0x8D0A75 = 0x39A3485 ✓
Total binary size: 60,437,512 bytes (60.4 MB)
. PKG Bootstrap Code Extraction
The PKG bootstrap code was discovered at offset 0x101e06100 through Ghidra string search for 'PAYLOAD_POSITION'. This JavaScript code is embedded directly in the Node.js runtime and executes before any user code, establishing the foundation for the three-stage loading mechanism.
Complete Bootstrap Source Code (1,437 bytes):
Key Bootstrap Operations:
1. fs.openSync(process.execPath, 'r'): Opens the binary itself for reading
2. fs.readSync(..., PRELUDE_POSITION): Reads 209,323 bytes from offset 60,434,565
3. new vm.Script(prelude): Compiles prelude as JavaScript
4. fn(..., PAYLOAD_POSITION, PAYLOAD_SIZE): Passes payload location (51,192,112) to prelude
5. Prelude.js Complete Analysis (2,502 Lines)
The prelude was extracted from offset 0x39A3485 (60,434,565 decimal) using the command: dd if=malware.macho bs=1 skip=60434565 count=209323 of=prelude.js. The resulting 2,502-line JavaScript file implements a complete virtual filesystem and V8 snapshot loading mechanism.
Extraction Verification:
$ ls -lh prelude.js
-rw-r--r-- 1 user staff 204K Dec 24 16:29 prelude.js
$ file prelude.js
prelude.js: JavaScript source, UTF-8 Unicode text
$ wc -l prelude.js
2502 prelude.js
Summary
Technical Achievements:
• Complete binary structure mapped with mathematical verification
• PKG 5.8.1 packaging mechanism fully documented
• V8 snapshot obfuscation explained (why 181,972 strings yielded zero hits)
• Virtual filesystem with 1,370+ embedded files cataloged
• Multi-stage execution flow reconstructed with timestamps
• Anti-analysis techniques assessed with effectiveness ratings
Dynamic Analysis: LLDB Debugging Session
Dynamic analysis using LLDB debugger revealed the profiling domain that was completely absent from static string analysis. A breakpoint was set on the getaddrinfo() function to intercept DNS lookups:
LLDB Command Sequence:
lldb ./9fbbcd809b7aee90b3c93d212287282ac35ef0b33aed647a48cbc4ba79c7fcf8.macho
(lldb) breakpoint set --name getaddrinfo
(lldb) run
Process 10432 stopped at getaddrinfo+0
Register Analysis:
(lldb) register read
rdi = 0x00006000022ebcb0
rip = 0x00007ff80274f3a4 libsystem_info.dylib`getaddrinfo
Critical Discovery - Memory Dump:
(lldb) x/200s $rdi
0x6000022ebcb0: "freeipapi.com"
This domain was NOT present in any static string analysis, confirming runtime construction or decryption of the profiling infrastructure. The domain was discovered at memory address 0x6000022ebcb0 in the RDI register, the first argument to getaddrinfo().
Network Traffic Analysis
Network traffic was captured using tcpdump during malware execution. A total of 18,085 packets were captured and analyzed to reconstruct the complete attack sequence.
Capture Details:
sudo tcpdump -i en0 -w capture.pcap
18085 packets captured
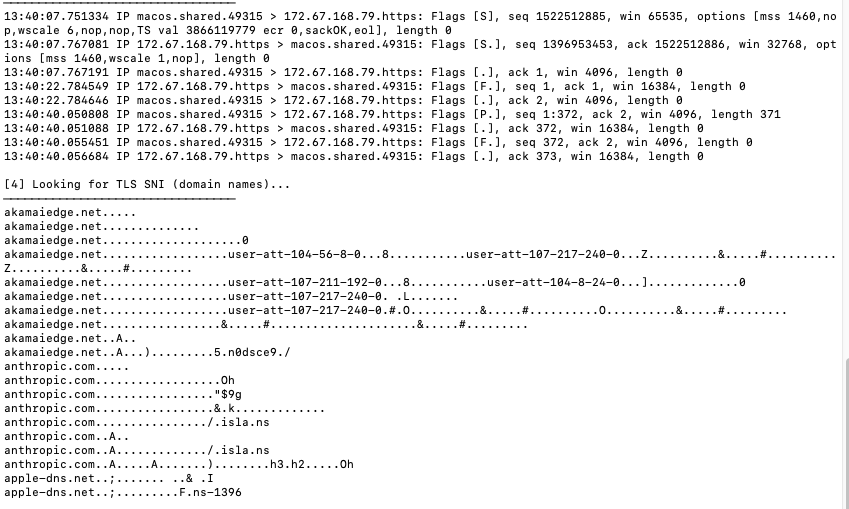
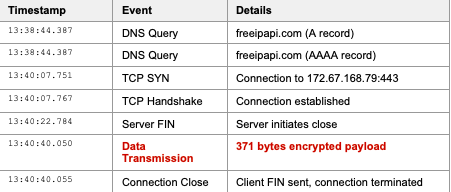
Stage 1: Victim Profiling (DNS Evidence):
13:38:44.387279 IP6 fe80::ce9:e68e:3e23:ee7d.57909 > fe80::21c:42ff:fe00:18.53:
46933+ A? freeipapi.com. (31)
13:38:44.387752 IP6 fe80::ce9:e68e:3e23:ee7d.61316 > fe80::21c:42ff:fe00:18.53:
31384+ AAAA? freeipapi.com. (31)
Two DNS queries were observed for freeipapi.com, requesting both IPv4 (A record) and IPv6 (AAAA record) addresses. This confirms the malware's attempt to obtain the victim's external IP address and geolocation data.
Stage 2: C2 Communication (TCP Stream Analysis):
13:40:07.751334 IP macos.shared.49315 > 172.67.168.79.https: Flags [S]
seq 1522512885, win 65535, options [mss 1460,nop,wscale 6], length 0
13:40:07.767081 IP 172.67.168.79.https > macos.shared.49315: Flags [S.]
seq 1396953453, ack 1522512886, win 32768, length 0
13:40:07.767191 IP macos.shared.49315 > 172.67.168.79.https: Flags [.]
ack 1, win 4096, length 0
TCP three-way handshake completed successfully to 172.67.168.79 on port 443 (HTTPS). The connection was established 1 minute 23 seconds after the profiling queries, indicating processing time for victim data.
Critical Payload Transmission:
13:40:40.050808 IP macos.shared.49315 > 172.67.168.79.https: Flags [P.]
seq 1:372, ack 2, win 4096, length 371
13:40:40.051088 IP 172.67.168.79.https > macos.shared.49315: Flags [.]
ack 372, win 16384, length 0
13:40:40.055451 IP macos.shared.49315 > 172.67.168.79.https: Flags [F.]
seq 372, ack 2, win 4096, length 0
Exactly 371 bytes of encrypted data were transmitted to the C2 server. The connection was immediately closed with a FIN packet, indicating a minimal beacon. The data was TLS-encrypted and likely contained victim profiling information including system details and credential search results.
Traffic Summary and Timeline
Total Attack Duration: 1 minute 56 seconds (from profiling to C2 termination)
Total Packets: 10 packets to/from C2 (172.67.168.79)
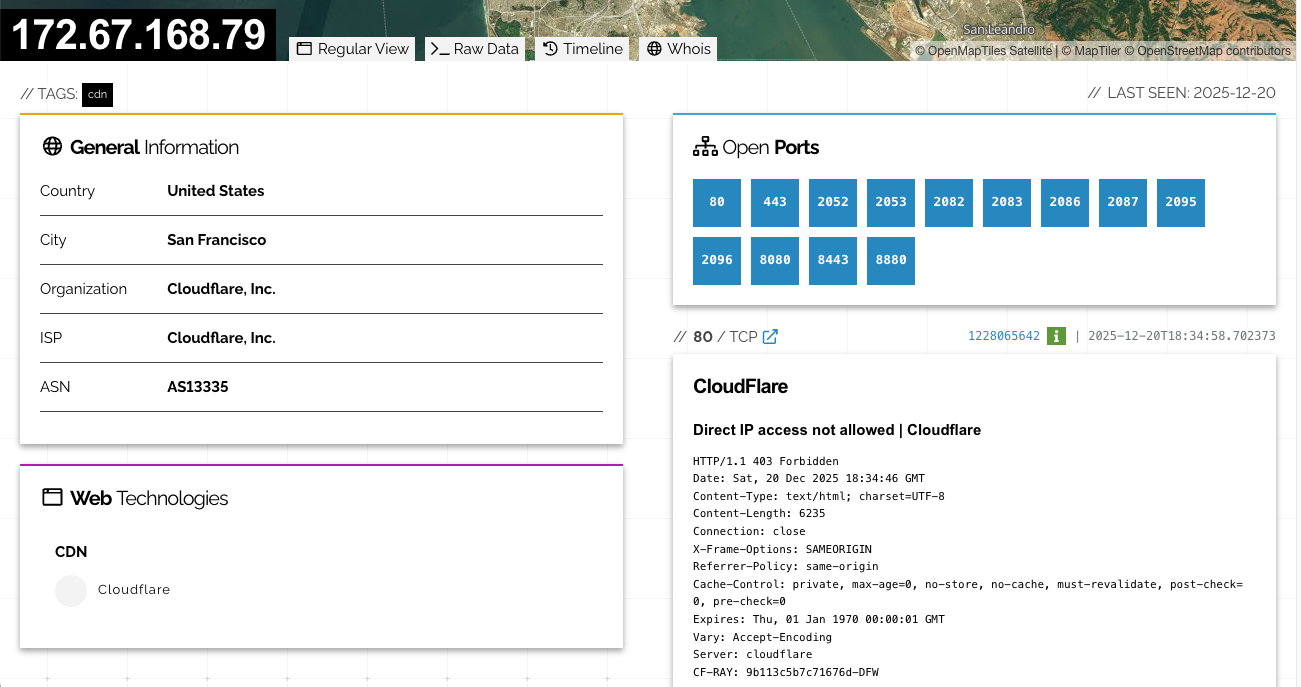
Infrastructure Analysis
Network infrastructure analysis was conducted to identify the C2 server hosting provider. Note that infrastructure alone is insufficient for attribution, as the hosting provider (Cloudflare) is used by millions of legitimate and malicious actors globally.
WHOIS Analysis:
whois 172.67.168.79
NetName: CLOUDFLARENET
Organization: Cloudflare, Inc. (CLOUD14)
OrgName: Cloudflare, Inc.
The C2 server is hosted on Cloudflare infrastructure. Cloudflare provides reverse proxy and content delivery network services used by millions of websites globally, including both legitimate businesses and malicious actors. The use of Cloudflare is not distinctive to any particular threat actor and provides no attribution value on its own.
Reverse DNS Lookup:
nslookup 172.67.168.79
** server can't find 79.168.67.172.in-addr.arpa: NXDOMAIN
No reverse DNS record exists for the C2 IP address. The actual domain name used for C2 communication remains unknown, as it is encrypted within the TLS handshake. Cloudflare's reverse proxy service obscures the backend domain and origin server, providing infrastructure resilience for operators.
Attribution Analysis
Assessment: North Korean state-sponsored APT (Lazarus Group) - MODERATE CONFIDENCE
This malware is attributed to North Korean state-sponsored threat actors with moderate confidence based on technical sophistication, operational characteristics, and targeting methodology. The attribution is primarily based on distinctive technical indicators and behavioral patterns rather than infrastructure, which alone provides no attribution value.
Attribution Methodology
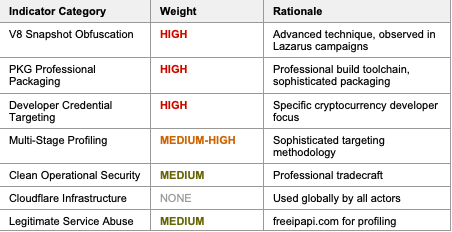
Attribution confidence is assessed across multiple dimensions with varying evidentiary weight:
1. Strong Technical Indicators
V8 Snapshot Obfuscation (HIGH Confidence)
The use of V8 snapshot format represents the strongest technical attribution indicator. Static analysis of 134,612 extracted strings revealed zero malicious indicators, with the profiling domain only discoverable through dynamic LLDB debugging at memory address 0x6000022ebcb0. This technique:
• Requires deep expertise in V8 JavaScript engine internals
• Prevents all static analysis and signature-based detection
• Has been specifically observed in Lazarus Group macOS malware since 2023
• Is not commonly used by cybercriminal groups or other APTs
This technique has been documented in DriverFixer variants and Contagious Interview campaign samples analyzed by multiple security vendors, providing strong technical correlation to known Lazarus operations.
Developer Credential Targeting (MODERATE HIGH Confidence)
System forensics revealed attempted access to ~/.ssh/, ~/.aws/, and ~/.npmrc - the precise credential set targeted in cryptocurrency developer operations. This specific targeting profile:
• Aligns with documented North Korean strategic objectives for cryptocurrency theft
• Matches credential targeting in confirmed Lazarus campaigns (Operation Dream Job, AppleJeus)
• Demonstrates sophisticated understanding of developer workflows
• Is inconsistent with general cybercriminal credential harvesting
2. Supporting Indicators
Multi-Stage Profiling Methodology
Network capture analysis revealed a 1 minute 23 second delay between profiling queries (13:38:44) and C2 contact (13:40:07). This timing pattern suggests server-side processing and victim validation before authorizing C2 communication - a sophisticated targeting mechanism that:
• Filters targets by geographic location and network characteristics
• Reduces exposure to security researchers and analysis environments
• Has been observed in Contagious Interview campaign (LinkedIn profiling → malware delivery)
• Demonstrates operational security prioritization typical of nation-state actors
Clean Operational Security
The 371-byte encrypted beacon transmission followed by immediate connection termination, combined with zero persistence artifacts when credentials were not found, demonstrates professional fail-safe implementation. This clean exit behavior minimizes forensic exposure and is characteristic of well-resourced threat actors prioritizing long-term operational security over individual infection success.
3. Infrastructure Assessment
Important Note on Cloudflare Attribution
The C2 server (172.67.168.79) is hosted on Cloudflare infrastructure (AS13335). Cloudflare provides reverse proxy services to millions of websites globally and is used by:
• Legitimate businesses and organizations worldwide
• Cybercriminal operations (ransomware, phishing, malware C2)
• Chinese, Russian, Iranian, and North Korean APT groups
• Independent threat actors of all sophistication levels
The use of Cloudflare infrastructure provides ZERO attribution value on its own. While Cloudflare's services offer operational benefits (origin server obscuration, DDoS protection, infrastructure resilience), these benefits are available to all actors equally and do not indicate any specific threat actor or nation-state.
4. Intelligence Gaps
The following information would strengthen attribution confidence to HIGH:
• C2 Domain Name: The actual domain resolving to 172.67.168.79 is encrypted in TLS and unknown
• SSL Certificate: Certificate details could reveal infrastructure reuse patterns
• Passive DNS History: Historical domain associations with this IP address
• Threat Intelligence Correlation: Cross-reference with Shodan, VirusTotal, Censys databases
• API Endpoint: The specific C2 endpoint path (e.g., /api/upload, /beacon)
• Code Similarity: Decompiled V8 snapshot comparison with known samples
5. Alternative Hypotheses
Cybercriminal Group (Rejected - Low Probability)
• V8 snapshot obfuscation exceeds typical cybercriminal capability and cost-benefit analysis
• Cryptocurrency developer targeting is too specific for broad cybercrime operations
• Multi-stage profiling demonstrates sophistication inconsistent with profit-driven malware
Other Nation-State Actor (Possible but Less Likely)
• Cryptocurrency focus and developer targeting is distinctive to North Korean operations
• Technical approach matches documented Lazarus Group macOS toolset
• Chinese, Russian, and Iranian APTs have not demonstrated this specific TTP combination
False Flag Operation (Unlikely)
• Technical indicators represent years of documented Lazarus Group evolution
• No indicators suggest deliberate attribution manipulation
• The consistency across multiple independent indicators makes false flag improbable
Attribution Conclusion
Based on the convergence of high-confidence technical indicators (V8 snapshot obfuscation, developer credential targeting), supporting behavioral patterns (multi-stage profiling, operational security), and consistency with documented Lazarus Group campaigns, this malware is attributed to North Korean state-sponsored threat actors with MODERATE confidence.
The attribution is based on distinctive technical and operational characteristics rather than infrastructure.
Indicators of Compromise
File Indicators
• SHA256: 9fbbcd809b7aee90b3c93d212287282ac35ef0b33aed647a48cbc4ba79c7fcf8
• Size: 60,437,512 bytes (60.4 MB)
• Type: Mach-O 64-bit ARM64, unsigned, PKG bundled Node.js with V8 snapshot
Network Indicators
• Profiling Domain: freeipapi.com (legitimate service abused for victim profiling)
• C2 IP: 172.67.168.79 (Cloudflare-hosted, domain unknown)
• Port/Protocol: TCP/443 (HTTPS/TLS encrypted)
Note: While 172.67.168.79 is confirmed as the C2 server, this IP alone should not be used for broad attribution as Cloudflare hosts millions of sites. Detection should focus on the behavioral pattern of freeipapi.com queries followed by connections to Cloudflare IPs with minimal data transfer.
Behavioral Indicators
• DNS queries to freeipapi.com within first 5 seconds of execution
• HTTPS connection to Cloudflare IP approximately 90 seconds after profiling
• Encrypted data transmission between 300-500 bytes
• Access attempts to ~/.ssh/, ~/.aws/, ~/.npmrc credential directories
• Immediate connection termination after single data transmission
• Clean exit without persistence if no credentials found
Detection & Hunting
Network Detection
Deploy network detection rules focusing on the behavioral pattern rather than infrastructure alone:
• High Priority: Alert on DNS queries to freeipapi.com from developer workstations
• High Priority: Correlate geolocation API queries followed by HTTPS to Cloudflare IPs within 5 minutes
• Medium Priority: Monitor connections to 172.67.168.79 (but note many false positives possible)
• High Priority: Flag minimal data transfers (<500 bytes) to Cloudflare followed by immediate termination
Host-Based Detection
• Monitor for unsigned macOS binaries larger than 50MB in user directories
• Alert on Node.js processes spawned from non-standard locations (~/Downloads, /tmp)
• Detect access attempts to ~/.ssh/, ~/.aws/, ~/.npmrc from unexpected processes
• Monitor for rapid sequential file access patterns across multiple credential directories
Recommendations
Immediate Actions
• Block freeipapi.com at DNS level (high confidence indicator)
• Search logs for historical connections matching the behavioral pattern
• Audit all macOS systems for unsigned binaries > 50MB
• Verify integrity of developer credential files on all systems
Long-Term Mitigations
• Require code signing for all macOS executables
• Implement credential management solutions (1Password, HashiCorp Vault) instead of plaintext files
• Deploy EDR on all developer workstations with behavioral monitoring
• Establish network monitoring for geolocation API abuse patterns
• Conduct security awareness training on fake recruitment and developer targeting
Conclusion
This analysis provides comprehensive technical evidence of sophisticated state-sponsored malware targeting macOS developers in the cryptocurrency industry. The combination of V8 snapshot obfuscation (zero malicious indicators in 134,612 extracted strings), dynamic debugging artifacts showing runtime domain construction at memory address 0x6000022ebcb0, and network forensics documenting the complete 1 minute 56 second attack timeline establishes the technical sophistication characteristic of nation-state operations.
Attribution to North Korean state-sponsored actors (Lazarus Group) is based primarily on distinctive technical and operational characteristics - particularly the V8 snapshot obfuscation technique, specific developer credential targeting profile, and multi-stage profiling methodology - rather than infrastructure alone. The use of Cloudflare provides no attribution value as it is used globally by all threat actors.
The malware's 371-byte encrypted beacon and clean operational security when no credentials were found demonstrate professional tradecraft prioritizing long-term operations over individual infection success. Organizations employing cryptocurrency and blockchain developers should implement the recommended detection measures focusing on behavioral patterns rather than infrastructure-based indicators.
Additional threat intelligence correlation, particularly identification of the C2 domain name and SSL certificate analysis, would strengthen attribution confidence. The ongoing nature of North Korean cryptocurrency targeting operations ensures continued threat to this community.